|
Global Aircraft -- E-3 Sentry
|
|
|
|
|
 |




|
|
Webmaster's Notes |
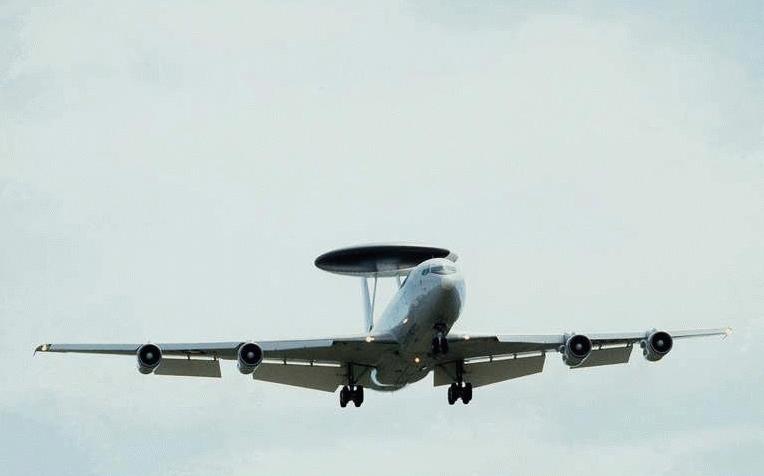
The Boeing E-3 Sentry is the West’s principal AWACS platform. The EC-137D prototype first flew on February 5, 1972, followed by the E-3A first flight on October 31, 1975. The E-3A
uses the 707-320B airframe and a massive payload of radar and electronic sensors. The E-3 can scan the skies of all aircraft and missiles and report what it sees electronically to all friendly aircraft, ground
fleet, satellites, and to any main headquarter bases. The E-3 is exported to many different countries including France, NATO, Saudi Arabia, and UK. France operates 4 E-3F, Saudi Arabia operates about 5
E-3A, the UK operates around 7 Sentry aircraft, NATO operates about 18 E-3A, and the USAF operates about 32 E-3.
|
|
E-3 Specifications
|
Primary Function Airborne surveillance, command, control and communications
Contractors, Prime: Boeing Aerospace Co.
Radar: Northrop Grumman
Power Plant Four Pratt and Whitney TF33-PW-100A turbofan engines
Thrust 21,000 pounds each engine
Length 145 feet, 6 inches (44 meters)
Wingspan 130 feet, 10 inches (39.7 meters)
Height 41 feet, 4 inches (12.5 meters)
Rotodome 30 feet in diameter (9.1 meters), 6 feet thick (1.8 meters), mounted 11 feet (3.33 meters) above fuselage
Speed Optimum cruise 360 mph (Mach 0.48)
Ceiling Above 29,000 feet (8,788 meters)
Maximum Takeoff Weight 347,000 pounds (156,150 kilograms)
Endurance More than 8 hours (unrefueled)
Unit Cost Approximately $270 million
Crew Flight crew of four plus mission crew of 13-19 specialists (mission crew size varies according to mission)
Date Deployed March 1977
Losses An E-3 crashed 22 Sep 1995 in Alaska, reducing the US fleet by one.
|
|
|
|
|
